Why Zirconia vs Emax Crowns Matters for Your Practice
Choosing between zirconia vs emax crowns is a practical decision that affects daily clinical results, not just material preference.
The right crown material helps you avoid common problems such as fractures, poor esthetics, occlusal adjustments, and remakes. The wrong choice often leads to extra chair time, patient dissatisfaction, and higher long-term costs. That is why understanding the real difference between zirconia and emax matters for every restorative case.
In simple terms, these two materials are used for different jobs. Zirconia crowns are known for strength and durability, especially in high-bite-force areas. Emax crowns are chosen for superior esthetics, particularly in the smile zone. The key is matching the material to the clinical situation, not using one material for every case.
This decision becomes even more important with digital workflows and faster turnaround expectations. Your crown material must work well with:
- Tooth position and bite force
- Esthetic expectations of the patient
- Tooth preparation design
- Cementation and margin control
- Lab consistency and manufacturing quality
For busy practices, material choice also impacts efficiency and cost control. A reliable material with predictable results reduces remakes and keeps cases moving on schedule. Over time, this directly improves profitability and patient trust.
This article explains zirconia vs emax crowns in a clear, case-focused way, so you can choose the right material with confidence and deliver stable, high-quality results for every patient.
What Are Zirconia Crowns?
Zirconia crowns are dental restorations made from zirconium dioxide, a ceramic material known for exceptional strength and durability. In modern dentistry, zirconia is widely used when reliability and long-term performance matter more than ultra-high translucency.
In simple terms, zirconia crowns are built to handle pressure. They perform extremely well in areas where bite force is high and where fractures or chipping would be unacceptable.
Key Characteristics of Zirconia Crowns
- Very high fracture resistance
- Strong performance under heavy occlusal load
- Stable margins and consistent fit with CAD/CAM workflows
- Long service life with low remake risk
Common Types of Zirconia Crowns
- Monolithic zirconia
One-piece construction, maximum strength, minimal chipping risk - Layered zirconia
Zirconia core with porcelain layering for improved esthetics - High-translucency zirconia
Improved appearance while maintaining good mechanical strength
Typical Clinical Indications
Zirconia crowns are commonly used for:
- Posterior teeth (molars and premolars)
- Patients with bruxism or strong bite force
- Crowns where minimal tooth reduction is preferred
- Cases where durability and predictability are the priority
From a practice and lab perspective, zirconia crowns are valued for their consistency. They mill accurately, tolerate minor prep variations, and reduce the risk of fractures during function. This makes them a dependable solution for high-volume practices that prioritize efficiency and long-term outcomes.
In short, zirconia crowns are the go-to choice when strength, stability, and predictable results are critical to your restorative success.
What Are Emax Crowns?
Emax crowns are dental restorations made from lithium disilicate, a glass-ceramic material known for its natural translucency and lifelike appearance. They are widely used when esthetics are the top priority and visual integration with natural teeth is critical.
In straightforward terms, emax crowns are designed to look as close to natural enamel as possible. They reflect and transmit light in a way that zirconia typically cannot fully match, especially in anterior and smile-zone restorations.
Key Characteristics of Emax Crowns
- Excellent translucency and color depth
- Natural-looking esthetic results
- Smooth surface finish with high patient acceptance
- Strong enough for single-unit restorations
Typical Clinical Indications
Emax crowns are commonly chosen for:
- Anterior teeth and visible smile-zone cases
- Patients with high esthetic expectations
- Veneers, inlays, onlays, and partial crowns
- Situations where conservative tooth preparation is possible
Practical Considerations for Your Practice
While emax crowns deliver superior esthetics, they are not designed for heavy bite-force situations. Compared to zirconia, they have lower fracture resistance and are generally not recommended for molars in bruxism cases or long-span restorations.
From a workflow perspective, emax crowns require precise preparation, accurate shade communication, and controlled cementation protocols. When these factors are managed correctly, they consistently produce high-value esthetic outcomes that patients immediately recognize.
In short, emax crowns are the preferred solution when appearance matters most and functional load is controlled, helping your practice deliver premium esthetic results with confidence.
Zirconia vs Emax Crowns: A Clear, Clinical Comparison
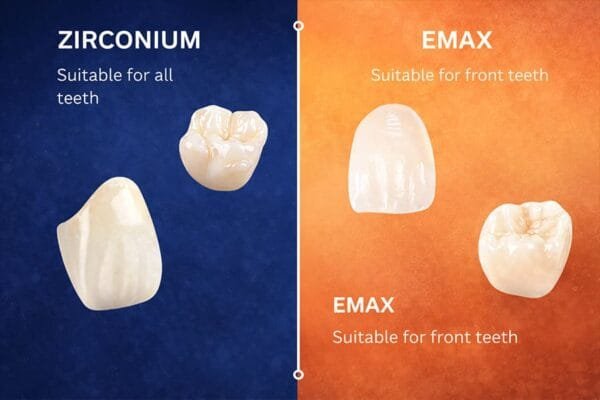
When evaluating zirconia vs emax crowns, the real difference is not marketing claims. It comes down to how each material behaves in the mouth and how reliably it supports your treatment goals. Below is a simplified, indication-driven comparison designed for everyday clinical decision-making.
Core Material Difference
- Zirconia is a polycrystalline ceramic built for mechanical strength and resistance to fracture.
- Emax is a glass-ceramic designed to mimic the optical properties of natural enamel.
This fundamental difference explains nearly every performance gap between the two materials.
Strength vs Esthetics
- Zirconia crowns excel in high-stress environments. They tolerate heavy occlusion, parafunctional habits, and posterior loading with minimal risk of failure.
- Emax crowns prioritize esthetics. Their translucency and light diffusion create a more natural appearance, especially in anterior teeth.
Practical takeaway: Zirconia protects function. Emax enhances appearance.
Indications by Tooth Location
- Posterior teeth: Zirconia is typically the safer, more predictable choice.
- Anterior teeth: Emax often delivers superior visual results when bite forces are controlled.
This is why many practices standardize zirconia for molars and reserve emax for smile-zone cases.
Preparation and Fit
- Zirconia is more forgiving with conservative preparations and minor variations, making it well suited for fast-paced digital workflows.
- Emax requires accurate reduction and margin design to achieve both strength and esthetics.
Workflow advantage: Zirconia supports efficiency and consistency; emax rewards precision.
Cementation and Longevity
- Zirconia crowns can often be cemented conventionally, simplifying chairside procedures.
- Emax crowns rely on adhesive bonding to reach optimal strength, adding technique sensitivity.
For practices focused on reducing chair time and variability, this difference matters.
Long-Term Reliability
- Zirconia delivers high predictability with low fracture rates over time.
- Emax performs well long-term when used in the right indication, but is less forgiving in high-load situations.
Bottom Line for Your Practice
The zirconia vs emax crowns decision is not about choosing one material over the other universally. It is about selecting the right tool for the job:
- Choose zirconia when durability, efficiency, and consistency matter most.
- Choose emax when esthetics are the primary driver and functional load is controlled.
When material selection aligns with indication and lab quality, outcomes become predictable, remakes decrease, and patient satisfaction increases. That is where clinical confidence and practice profitability meet.
Below is a clear, specification-based comparison table designed to support faster, more confident material selection. This data reflects commonly accepted clinical ranges used by dental labs and manufacturers, translated into practical value for your daily cases.
| Specification | Zirconia Crowns | Emax Crowns (Lithium Disilicate) |
| Material Type | Polycrystalline ceramic (Zirconium Dioxide) | Glass-ceramic (Lithium Disilicate) |
| Flexural Strength | ~900–1,200 MPa (varies by translucency grade) | ~360–400 MPa |
| Fracture Toughness | Very high | Moderate |
| Translucency | Medium to high (depending on zirconia type) | Very high, enamel-like |
| Esthetic Performance | Good to very good | Excellent |
| Minimum Tooth Reduction | ~0.5–0.8 mm | ~1.0–1.5 mm |
| Ideal Tooth Location | Posterior, full-arch, high-load areas | Anterior, smile zone |
| Bruxism Suitability | Highly recommended | Not recommended |
| Opposing Tooth Wear | Low when properly polished | Low |
| Cementation Method | Conventional or resin-modified cement | Adhesive resin bonding |
| Technique Sensitivity | Low | High |
| Margin Forgiveness | High | Moderate |
| Typical Use Cases | Molars, premolars, bridges, implant crowns | Anterior crowns, veneers, inlays/onlays |
| Remake Risk | Low | Moderate if case selection is poor |
| Lab Manufacturing Consistency | Very high with CAD/CAM | High but more esthetic-sensitive |
| Average Turnaround Stability | Strong, scalable | Slightly longer due to esthetic steps |
| Cost Positioning | Cost-efficient for high volume | Premium esthetic solution |
Why SF Dental Lab Is the Right Partner for Zirconia and Emax Crowns
When material choice directly impacts outcomes, the lab you work with matters as much as the crown itself. SF Dental Lab is built to help you make the right decision between zirconia vs emax crowns—case by case, not by default.
Case-Driven Material Guidance
At SF Dental Lab, every case is evaluated with a practical mindset:
- Tooth position, occlusion, and functional load
- Preparation design and available reduction
- Esthetic expectations and shade complexity
- Risk factors such as bruxism or limited clearance
This approach helps ensure zirconia is used where durability is critical and emax is selected when esthetics truly matter.
Advanced Digital Workflow
SF Dental Lab operates on a fully integrated digital workflow:
- Seamless support for intraoral scans and CAD/CAM systems
- Material-specific design protocols for zirconia and emax
- Consistent milling and finishing for predictable fit
The result is fewer adjustments, smoother delivery, and reliable outcomes across cases.
Strict Quality Control Standards
Quality is controlled at every step:
- Precise margin inspection and internal fit verification
- Strength validation for zirconia restorations
- Detailed esthetic checks for emax translucency and shade matching
This reduces remakes and protects your clinical results.
Reliable Turnaround and Scalability
SF Dental Lab is structured to support both single practices and growing DSOs:
- Stable turnaround times
- Consistent results across case volumes
- Clear communication from case planning to delivery
Practical Takeaway
Choosing between zirconia vs emax crowns is easier when you have the right lab partner. SF Dental Lab helps you select the right material, execute it with precision, and deliver restorations that meet functional, esthetic, and business expectations—consistently and confidently.
Work With a Dental Lab That Supports Better Crown Outcomes
More practices are choosing a dental lab in china because it offers a strong balance of quality, efficiency, and scalability. With modern digital workflows and experienced technicians, the right lab partner can deliver reliable zirconia and emax crowns without compromising clinical standards.
When quality control and communication are handled properly, working with a dental lab in China becomes a practical advantage. Consistent fit, stable turnaround times, and predictable results help reduce remakes and keep cases on schedule.
At SF Dental Lab, this approach is focused on one outcome: helping your practice deliver durable, esthetic crowns with confidence—case after case.